WELCOME TO REACON
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Insulators are devices installed between conductors of different potentials or between conductors and grounding components, capable of withstanding voltage and mechanical stress. There are various types and shapes of insulators. Although there are significant differences in the structure and appearance of different types of insulators, they are all composed of two main parts: insulation components and connecting fittings.
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
Strain insulator for lines
The Strain Insulator for Lines is designed to provide reliable electrical insulation and strong mechanical tension support in overhead power transmission and distribution systems. This strain insulator for overhead lines is installed at dead-end points, sharp line angles, and tension sections, where conductors are subjected to high mechanical loads. Available in porcelain or polymer types, the strain insulator ensures stable performance, excellent insulation, and long service life in outdoor environments.
High mechanical strength for conductor tension
Excellent electrical insulation performance
Suitable for dead-end and angle line sections
Porcelain or polymer options available
Strong resistance to weather and pollution
Long service life with low maintenance
Widely used in transmission and distribution lines
1. Rich experience in ODM and OEM
2. Excellent One-stop service
3. High Quality Precision Customized forging & Casting services
4. The lowest price
5. Strict quality control
6 We can manufacture it according to customers requirements.


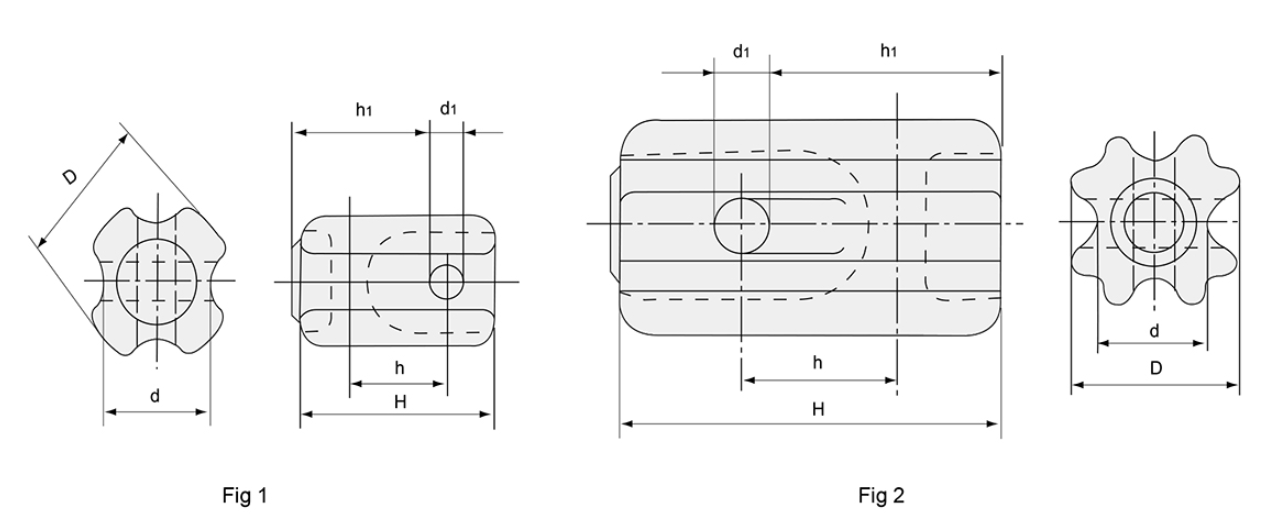
| Fig | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| CIass ANSI | 54-1 | 54-2 | 54-3 | 54-4 | ||
Main Dimensions (mm) | H | 88 | 108 | 140 | 171 | |
| h | 44 | 57 | 79 | 69 | ||
h1 | 64 | 76 | 103 | 114 | ||
| D | 64 | 73 | 86 | 89 | ||
| d | 44 | 54 | 60 | 60 | ||
| d1 | 16 | 22 | 25 | 25 | ||
| Mechanical failing load (kV) | 44 | 53 | 89 | 89 | ||
| Creepage Distance(mm) | 41 | 47 | 57 | 76 | ||
| Flashover voltage | Power-frequency | Dry (kv) | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| Wet (kV) | 12 | 15 | 18 | 23 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 0.43 | 0.63 | 1.2 | 2 | ||
Overhead transmission lines
Power distribution lines
Dead-end conductor sections
Large-angle line turns
High-tension line sections
• Install the strain insulator for lines at locations where conductors are terminated or change direction.
• Connect conductors to the insulator using strain clamps or dead-end fittings.
• Ensure correct alignment to evenly distribute mechanical tension.
• Inspect periodically to confirm mechanical integrity and insulation condition.
Manufactured with high-quality insulating materials
Strict mechanical load and electrical testing
Stable performance for outdoor service
Consistent quality control before shipment
Designed to meet utility application requirements
Q1: What is a strain insulator for lines used for?
A1: It is used to support conductor tension and provide electrical insulation at dead-end or angle points.
Q2: Where is a strain insulator typically installed?
A2: It is installed at dead ends, sharp angles, and high-tension sections of overhead lines.
Q3: Can strain insulators be used outdoors?
A3: Yes, they are designed for long-term outdoor operation.
Q4: What materials are available for strain insulators?
A4: Common materials include porcelain and polymer composite.
Q5: Do strain insulators require frequent maintenance?
A5: No, only routine inspection is required under normal conditions.